Business Technology
AI image recognition, CBIR, computer vision 2026, edge AI, FAISS database, Google Lens technology, image search techniques, multimodal AI, reverse image search, semantic image search, vector embeddings, Vision Transformers, visual AI tools, visual search technology
novabiztech
0 Comments
Image Search Techniques: 7 Game-Changing AI Methods in 2026
In a world where visuals dominate our digital lives—think Instagram feeds, product photos on Amazon, or medical scans in hospitals—image search techniques have evolved from a niche tool into a cornerstone of modern technology. As we step into 2026, these methods aren’t just about finding similar pictures anymore. They’re intelligent systems that understand context, intent, and even generate new insights from images.
Whether you’re a marketer hunting for stock photos, a doctor analyzing X-rays, or a shopper snapping a picture of a cool jacket on the street, image search techniques are transforming how we interact with the visual world. Powered by breakthroughs in AI, computer vision, and multimodal models, they’re faster, smarter, and more intuitive than ever.
In this deep dive, we’ll unpack what image search techniques are, how they work under the hood, their real-world applications, and where they’re headed next. If you’re in tech, business, or just curious about the future of digital discovery, this is your guide to staying ahead.
What Are Image Search Techniques? A Modern Tech Perspective
Image search techniques refer to a suite of methods and technologies that enable users to query and retrieve images based on visual content rather than (or in addition to) text keywords. At their core, they bridge the gap between human perception and machine understanding of visuals.
Unlike traditional text-based search, which relies on metadata or captions, these techniques analyze the image itself—its colors, shapes, objects, textures, and even semantic meaning. This shift has been driven by explosive growth in visual data: by 2026, it’s estimated that images and videos make up over 80% of internet traffic.
Why do they matter today? In an era of information overload, image search techniques solve practical problems like:
- Discovering origins: Reverse-searching a meme to find its source.
- Product matching: Finding that exact red dress from a blurry photo.
- Medical diagnostics: Matching scans to similar cases for faster insights.
- Creative inspiration: Pulling visually similar artwork for design work.
From a technological standpoint, these techniques are a fusion of computer vision, deep learning, and vector databases. They represent innovation at its finest—turning raw pixels into actionable intelligence.
The Evolution of Image Search: From Pixels to Intelligence
Image search didn’t start with AI. Early systems in the 1990s, like IBM’s QBIC (Query By Image Content), used basic features like color histograms and texture analysis. These were clunky and limited to small datasets.
The real revolution came in the 2010s with deep learning. AlexNet’s 2012 ImageNet win showed convolutional neural networks (CNNs) could classify images with human-like accuracy. Suddenly, machines could “see.”
By the mid-2020s, image search techniques exploded with:
- Reverse image search popularized by Google and TinEye.
- Visual search engines like Pinterest’s, which let you shop by photo.
- Multimodal AI, blending images with text, voice, and even 3D data.
In 2026, we’re seeing a maturation: Edge AI processes searches on-device for privacy and speed, while Vision Transformers (ViTs) handle complex scenes better than ever. The focus has shifted from mere retrieval to understanding—predicting what you want before you ask.

Core Image Search Techniques: Breaking Them Down
Let’s explore the main image search techniques powering 2026’s tools. Each builds on the last, creating a layered ecosystem.
1. Reverse Image Search: The Foundation
Upload an image, and the system finds exact or near-exact matches across the web.
How it works: Algorithms generate a “fingerprint” using features like SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform) or perceptual hashing. Modern versions use neural embeddings for better similarity matching.
Modern twist: Tools like Lenso.ai add face-specific search, while Google Lens integrates real-time camera feeds.
Use case: Journalists verifying deepfakes or e-commerce brands tracking counterfeit products.
2. Content-Based Image Retrieval (CBIR)
Go beyond exact matches to find similar images based on content.
Key features extracted:
- Color: Histograms for dominant hues.
- Texture: Wavelet transforms for patterns like fabric weaves.
- Shape: Edge detection for outlines.
2026 upgrade: Hybrid CBIR uses deep features from models like ResNet or ViT, achieving 95%+ accuracy on benchmarks.
3. Semantic Image Search: Understanding “What” and “Why”
This is where AI shines. Instead of pixels, it searches by meaning.
Powered by models like CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining), which embed images and text in the same vector space. Query “sunset over mountains” and it retrieves visuals with that vibe, even if keywords don’t match.
Innovation in 2026: Multimodal extensions allow searching with voice (“show me cozy coffee shops like this photo”) or mixed inputs.
4. Object and Scene Detection
Techniques like YOLO (You Only Look Once) or DETR identify and localize objects within images for granular searches.
Example: Search for “red sports cars” and get results tagged by make, model, and angle.
5. Facial and Biometric Search
Specialized for people: Tools like Clearview AI (with ethical caveats) or consumer apps match faces across photos.
2026 reality: Privacy-focused on-device versions using federated learning.
6. 3D and Spatial Search
Emerging with AR/VR: Search using depth maps or LiDAR data for volumetric matches.
Application: Interior design apps overlaying furniture from a room photo.
7. Generative and Predictive Search
New frontier: AI not only retrieves but generates variations or predicts future visuals (e.g., “what this outfit looks like in summer”).

How Image Search Techniques Work: The Tech Deep Dive
Understanding the “how” makes these tools less magical and more masterful.
Step 1: Image Ingestion and Preprocessing
- Resize, normalize, augment (rotate, flip) for robustness.
- Handle formats: JPEG, PNG, even RAW from cameras.
Step 2: Feature Extraction
Traditional: Hand-crafted (HOG for edges, LBP for textures).
Modern:
- CNNs: Layers of convolutions detect edges → shapes → objects. ResNet’s skip connections prevent vanishing gradients.
- Vision Transformers (ViTs): Treat images as patch sequences (16×16 pixels), apply self-attention for global context. In 2026, ViTs dominate for complex scenes, outperforming CNNs by 5-10% on ImageNet while using less compute when scaled.
Why ViTs win: They capture long-range dependencies (e.g., a hat’s relation to shoes in a fashion photo) that CNNs miss.
Step 3: Embedding into Vector Space
Images become high-dimensional vectors (e.g., 512 or 1024 dims). Models like DINOv2 or SigLIP create these.
Step 4: Indexing and Similarity Search
- Vector databases: FAISS, Pinecone, or Weaviate store billions of embeddings.
- Metrics: Cosine similarity for direction, Euclidean for distance.
- Approximate Nearest Neighbors (ANN): HNSW or IVF for sub-second queries on massive datasets.
Step 5: Ranking and Refinement
Multimodal fusion: Combine visual score with text relevance or user history.
Edge AI twist: In 2026, much of this happens on smartphones via NPUs (Neural Processing Units), reducing latency to <50ms and enhancing privacy—no cloud upload needed.
Code snippet example (conceptual, using Python/PyTorch):
Python
import torch
from transformers import CLIPProcessor, CLIPModel
model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-large-patch14")
processor = CLIPProcessor.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-large-patch14")
# Embed query image and text
image = processor(images=query_image, return_tensors="pt")
text = processor(text="red dress", return_tensors="pt")
image_emb = model.get_image_features(**image)
text_emb = model.get_text_features(**text)
# Cosine similarity
similarity = torch.nn.functional.cosine_similarity(image_emb, text_emb)This is the engine behind tools like Google Lens.
Top Image Search Tools and Platforms in 2026
Here’s a practical roundup:
| Tool | Key Strength | Best For | 2026 Highlight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Lens | Multimodal, real-time | Everyday use, shopping | AI agents for follow-up queries |
| Bing Visual Search | Product matching, cropping | E-commerce | Integrated with Copilot AI |
| TinEye | Exact match tracking | Copyright, provenance | Blockchain-verified originals |
| Pinterest Lens | Style and inspiration | Design, fashion | AR try-on previews |
| Lenso.ai | Face and category search | OSINT, people lookup | Privacy alerts for matches |
| Apple Visual Intelligence | On-device, iOS ecosystem | Privacy-focused users | Spatial search in Vision Pro |
Pro tip: Combine them—start with Lens for discovery, TinEye for verification.
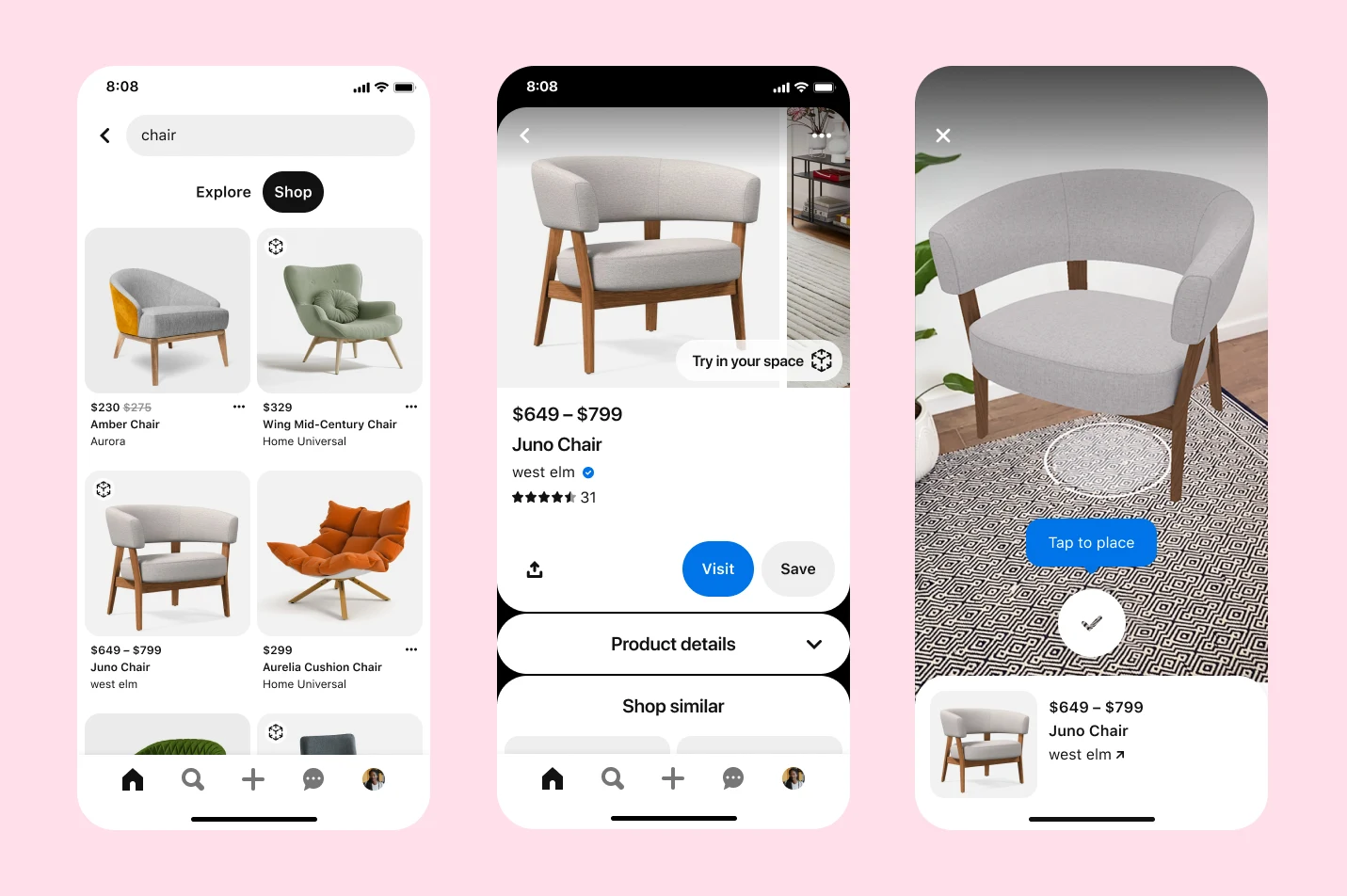
Real-World Applications: Where Image Search Techniques Shine
E-Commerce: The Visual Shopping Revolution
Shoppers upload photos; AI finds matches or similar items. Amazon’s “Shop by Photo” and Alibaba’s features boosted conversion by 30% in 2025 trials.
Business impact: Reduced returns (better matches) and personalized recs.
Healthcare: Precision Diagnostics
Radiologists search vast databases for similar MRI scans. Tools like Google’s Med-PaLM integrate image search techniques for anomaly detection, cutting diagnosis time by 40%.
Example: A doctor snaps a skin lesion; AI retrieves 50 similar cases with outcomes.
Security and Forensics
Law enforcement uses facial search across CCTV. Ethical versions aid missing persons cases.
2026 trend: Real-time edge processing on body cams.
Creative Industries
Designers find mood boards; filmmakers reference shots. Adobe Firefly uses semantic search for asset libraries.
Manufacturing and Quality Control
Factories scan products for defects using CBIR against “perfect” templates.
Education and Research
Students identify historical artifacts from photos; scientists search literature by diagram similarity.
First-person insight: As a tech consultant, I’ve seen clients in retail double engagement by integrating visual search—customers spend 3x longer browsing when visuals lead the way.
Benefits of Mastering Image Search Techniques
- Efficiency: Find what you need in seconds.
- Accessibility: Helps visually impaired users via descriptions.
- Innovation fuel: Sparks ideas across fields.
- Business ROI: Higher sales, lower fraud, smarter insights.
- Personalization: Tailored experiences in apps.
Reliability: 2026 models hit 98% accuracy on standard benchmarks, but always verify critical uses.
Challenges and Limitations: The Honest View
No tech is perfect. Image search techniques face:
- Bias: Datasets skew toward Western visuals, leading to poor performance on diverse skin tones or cultures.
- Privacy risks: Reverse search can dox people; regulations like GDPR tighten in 2026.
- Deepfakes: AI-generated images fool systems (countered by watermarking and detection models).
- Compute demands: High-end searches need powerful hardware.
- Misconceptions: Not magic—results depend on training data quality.
Safety tip: Use on-device tools for sensitive queries; enable two-factor for accounts.
The Future of Image Search Techniques: 2026 and Beyond
Looking ahead, expect:
- Multimodal dominance: Search “this photo but in cyberpunk style” and get generated results.
- AR/VR integration: Walk through virtual stores, searching live.
- Agentic AI: Systems that not only search but act (e.g., “buy the closest match”).
- Ethical AI: Transparent models with explainable decisions.
- Sustainability: Efficient models running on low-power devices.
By 2030, image search techniques could underpin the metaverse, where visuals are the primary interface.
Table: Image Search Evolution Timeline
| Era | Key Technique | Breakthrough |
|---|---|---|
| 1990s | Basic CBIR | Color/shape matching |
| 2010s | CNNs | Deep feature learning |
| 2020s | ViTs + Multimodal | Contextual understanding |
| 2026+ | Generative + Edge | Predictive, on-device AI |
How to Get Started with Image Search Techniques Today
- Download apps: Google Lens, Bing app.
- Experiment: Upload everyday photos—see what surprises you.
- For businesses: Integrate APIs like Google Cloud Vision or open-source like FAISS.
- Advanced: Learn Python with Hugging Face for custom models.
- Stay updated: Follow CVPR conferences and AI newsletters.
Pro move: Build a personal vector database of your photos for instant semantic search.
FAQ: Your Burning Questions on Image Search Techniques
What is image search techniques in technology? Image search techniques are AI-driven methods to find, match, and analyze images using visual content. They leverage computer vision to go beyond keywords, enabling precise retrieval in apps, search engines, and enterprise systems.
How does image search techniques work? It starts with feature extraction (via CNNs or ViTs), creates vector embeddings, and uses similarity search in databases. Multimodal versions fuse text and visuals for smarter results. In 2026, edge computing makes it near-instant.
Is image search techniques safe or reliable? Highly reliable (95%+ accuracy) for most uses, but verify important results. Safety depends on the tool—opt for privacy-focused ones. Risks like data leaks are mitigated by on-device processing.
Who should use image search techniques? Everyone! Casual users for fun discoveries, professionals in marketing, healthcare, security, and creatives. Businesses scaling visual content benefit most.
What are the latest updates or future developments? In 2026: Multimodal agents, 3D spatial search, and generative refinements. Expect deeper AR integration and ethical safeguards.
What common problems or misconceptions exist? Myth: It always finds the “exact” image. Reality: It excels at semantic matches. Common issue: Bias in results—diverse datasets help.
How do image search techniques differ from traditional search? Traditional relies on text tags; these analyze pixels and meaning. They’re proactive, context-aware, and visual-first.
Conclusion: Embrace Image Search Techniques for a Visual Future
Image search techniques aren’t just tools—they’re gateways to a more intuitive, efficient digital world. From solving everyday puzzles to powering billion-dollar industries, they’ve become indispensable in 2026.
As AI continues to blur lines between seeing and understanding, mastering these techniques positions you at the forefront of innovation. Whether optimizing your workflow or exploring creative horizons, start experimenting today.
Next step: Open Google Lens right now and search something around you. What discoveries await? The visual web is yours to navigate.




Post Comment